Pool Contract
At the center of Bend is the Pool smart contract. This smart contract serves as the main user-facing contract of the protocol, and it coordinates with subsidiary logic contracts to carry out the execution. The main user functions of Pool.sol are illustrated below:
Core Functions
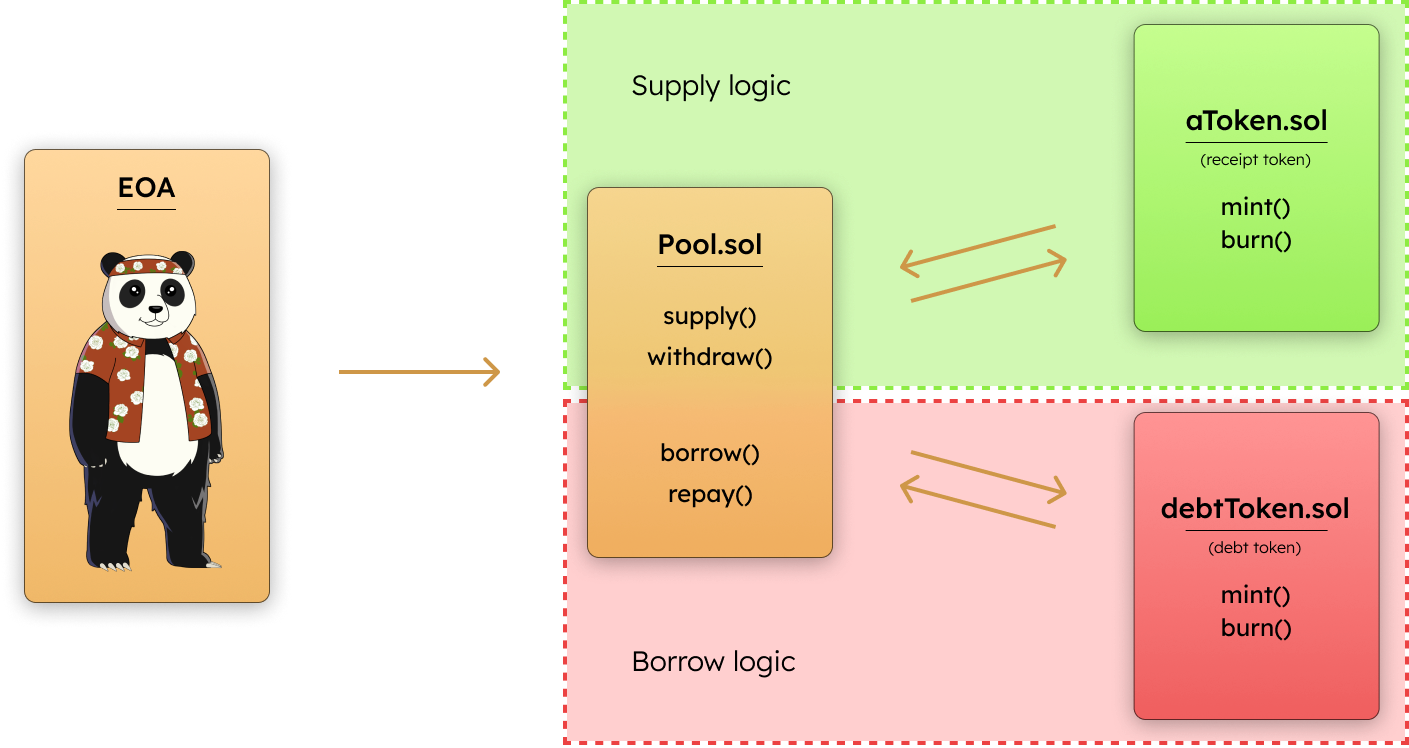
The core functions of Bend are separated into two categories, and governed by distinct logic contracts:
- Supply - governed by
SupplyLogic.sol - Borrow - governed by
BorrowLogic.sol
Supply - relates to suppliers providing and removing liquidity from the protocol. aTokens, which represent users' entitlement to withdraw their supplied liquidity, are minted and burned during liquidity provision and removal, respectively.
Borrow - refers to borrowers borrowing and repaying loans. DebtTokens, which represent the users' outstanding debt, are minted and burned during borrowing and repayment, respectively.
Pool Interactions
The below diagram illustrates how Pool’s main functions interact with lower level functions.
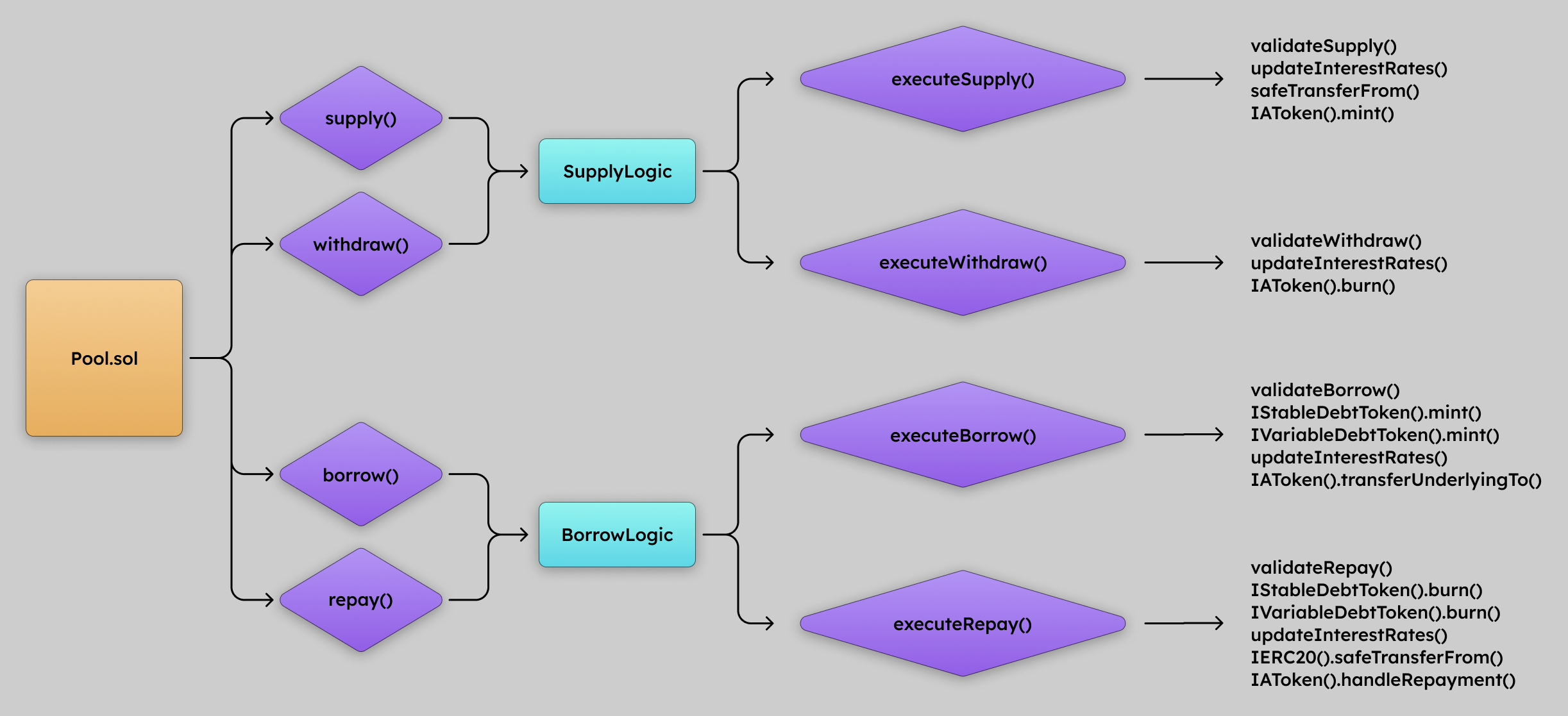
Note: the
Poolcontract mainly makes these subsequent calls to internal functions (e.g.executeSupply()withinSupplyLogic.sol).
Other Pool Functions
Liquidation
Liquidations are crucial for ensuring the solvency of Bend and to avoid users from the protocol accruing bad debt. Liquidations are controlled by the LiquidationLogic contract.
Developers may consult the Liquidations Guide for more information on executing liquidations.